Blockchain's KYC Renaissance: Reshaping Due Diligence for the Digital Era
Jul 20, 2023
Introduction
KYC (Know Your Customer) is the process by which financial institutions (FIs) obtain information about the identity and address of the customer. The process of performing due diligence for verifying the identity of existing and new clients is governed by a regulator. It is a measure to prevent misuse of the FI's services, such as money laundering, terrorist financing, financial fraud, etc. The KYC processes continue to become increasingly stringent and complex, as per the requirements set by banking regulatory bodies, law enforcement agencies, and international organizations. To meet them, FIs spend huge amounts of money and effort on KYC-related procedures. Failure to comply with KYC regulations entails significant risks and penalties for financial institutions. In 2020 alone, several global institutions were fined $10.4 billion for anti-money laundering (AML), KYC, and data privacy violations. Despite the cost and effort required for the process, it remains manual and time-consuming, repetitive, prone to error, and fails to meet the needs of both the customers and FIs. Blockchain is an emerging technology that is a decentralized ledger of all transactions across a peer-to-peer network. It is now used in many industries to build trust and transparency through an immutable provenance. A blockchain-based architecture, offering immutability and cutting-edge security features, is a modern and elegant solution to the problems of a traditional KYC process. It can deliver better compliance outcomes, efficiency, and customer experience.KYC and due diligence using blockchain
In a traditional KYC and due diligence system, each FI conducts a detailed identity check of its users through an individual organization or a government structure. However, this process requires significant time and effort. Blockchain is an emerging technology that is a decentralized ledger of all transactions across a peer-to-peer network. It is now being used in various industries to foster trust and transparency through indestructible authenticity. This allows the creation of a shared system in which users go through the KYC procedure to authenticate their identity only once. Other FIs or agencies working in collaboration can access the same data with the customer's permission. However, not all blockchain platforms are suitable for all purposes. As per research, distributed ledger technology (DLT), a private model seeking users' permission, is the most suitable for KYC processes.KYC process on the blockchain
Here is a high-level overview of how a blockchain KYC system can assist in this scenario.User Profile Creation
Financial Institution (FI-1) deploys a blockchain-based KYC platform. The user completes the one-time process with their identity documents. The uploaded is now accessible to FI-1 for verification.Transactions with FI-1
When a user transacts with FI-1, they allow access to their digital profile. FI-1 saves a copy of the data on their server after validating it. A hash function is designated to the data uploaded on the DLT platform. Digital copies of the KYC details are added to the user's profile by FI-1. The copies are embedded with a hash function, which corresponds to the hash function on the DLT platform.Transactions with FI-2
When FI-2 wants to conduct KYC for the same user, the user grants them access to their previously created profile. The available data and its hash function are then compared to the hash function uploaded by FI-1. If both the hash functions match, it confirms the information is valid. If they don't match, FI-2 must validate the customer's KYC documents manually. Whenever the customer updates the KYC documents (a new passport/driving license etc.), there are smart contracts that automatically update the systems. The document/s submitted to FI-1 are broadcasted across the blockchain through a new hash function. This information is then accessible to the other participants. Unlike the traditional digital KYC process, FI-2 is not required to conduct a separate KYC verification process for the same customer. Instead, they can take information from the blockchain to conclude the customer's second KYC transaction.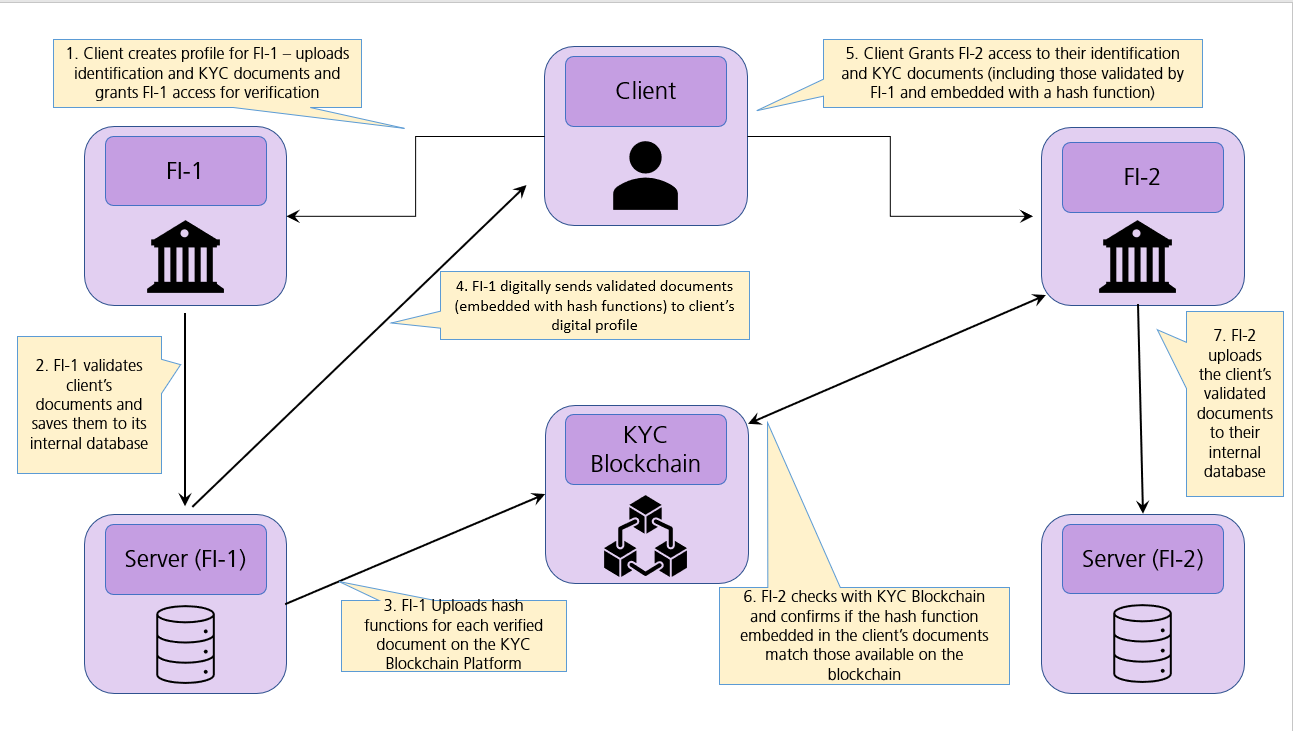
Example of a Blockchain-based KYC Process
Advantages of a blockchain-based KYC and due diligence process
Distributed data collection - In a blockchain KYC system, data is placed on a decentralized network that can be accessed with permission. This ensures data security and prevents unauthorized access. Improved operational efficiency - In the early stages of KYC, unhackable digital processes and a permission-based network reduce the effort and time considerably. Eventually, it makes the customer onboarding process shorter and reduces regulatory and compliance costs. Validated information accuracy - A blockchain KYC system allows financial institutions to check the data's reliability, reducing the time and effort spent gathering this information. User data updated in real-time - The details of a KYC transaction completed at an FI are shared on a distributed ledger. The blockchain system allows other institutions to access this updated information in real-time. All the collaborators on the system are updated about any modifications or additions to the data.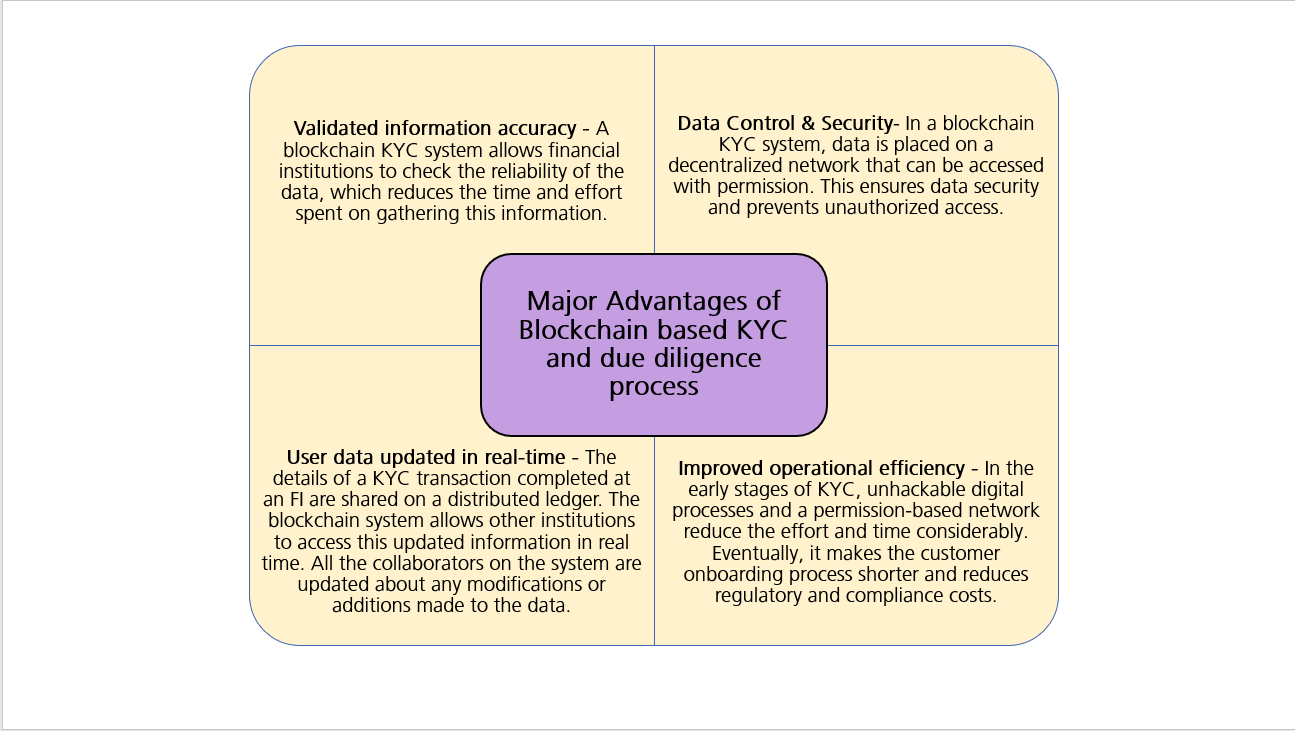
Some challenges of blockchain-based KYC and due diligence process
- KYC practices vary widely depending on the institution and location due to the lack of standardized KYC procedures. This produces repetitive effort and inhibits the capacity of multiple FIs to reap the benefits of a blockchain-based KYC efficiently.
- Customers are concerned about their information being accessible to financial institutions they do not conduct business with frequently. This raises a data privacy red flag for regulators.
- The cryptographic transactions performed in a blockchain-based KYC consume a significant amount of time and resources. It may not be the best option for continuous KYC verification,i.e.ongoing checks and monitoring of customer transactions.
